Getting Started: Integrating M8325 BLDC Motor with NDrive Z1 using the Onboard Encoder
This tutorial provides a step-by-step walkthrough to set up, configure, and operate the NDrive Z1 with the M8325 BLDC motor using the onboard 14-bit absolute encoder and a 2Ω/50W brake resistor.
Introduction
This tutorial provides a step-by-step procedure for connecting and configuring the M8325 BLDC motor with the NDrive Z1 using the onboard 14-bit absolute encoder. The procedure includes hardware connections, brake resistor integration, CAN communication setup via the NLink adapter, and initial parameter configuration through the NMotion CLI Tool. Once you complete the steps, the motor will be calibrated and ready to use.
What You Need
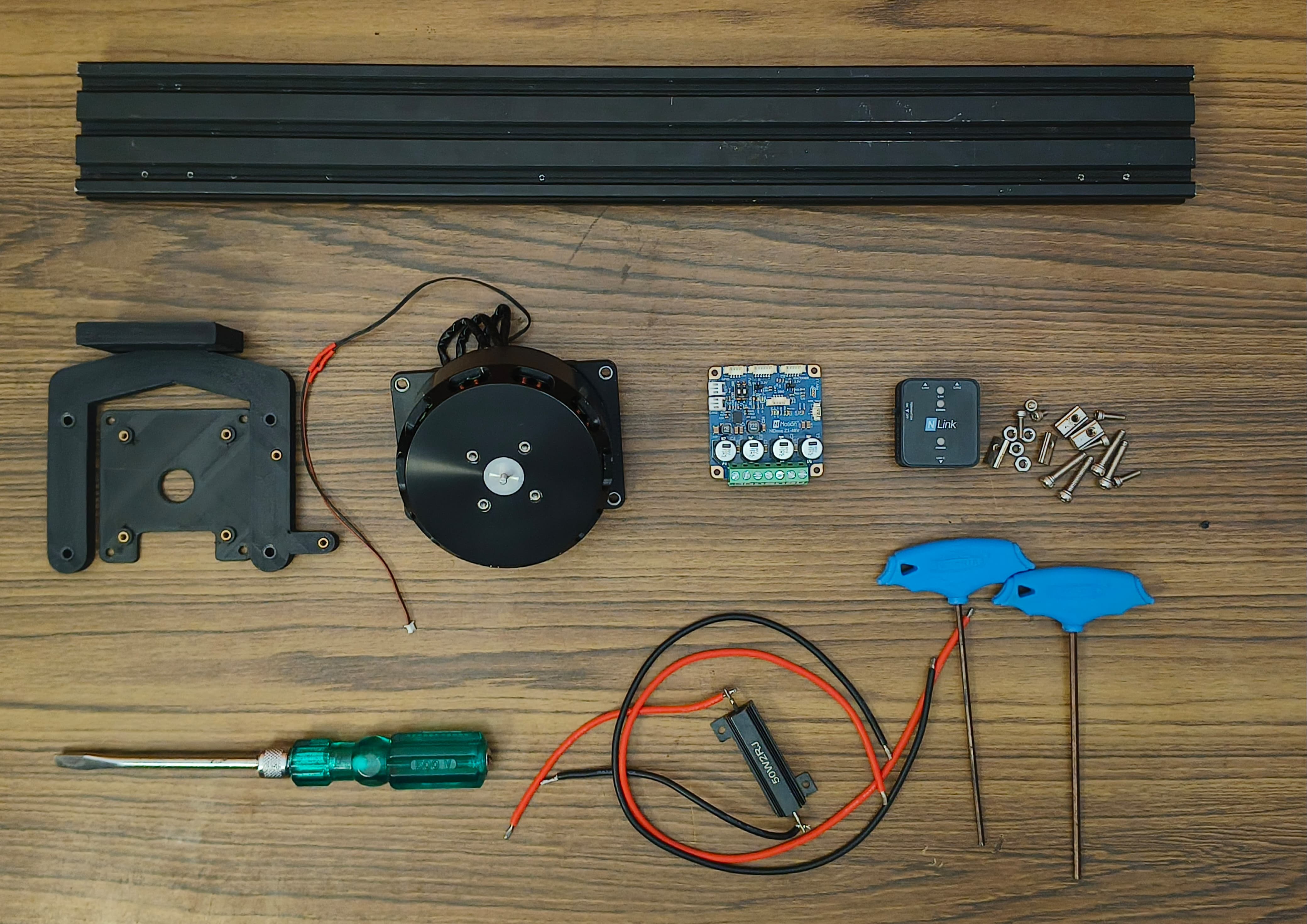
Before diving into wiring and configuration, make sure you have all the essential components and tools required to integrate the NDrive Z1 with the M8325s 100 kV BLDC motor.
NMotion Components
- NDrive Z1 Motor Driver
- NLink Adapter (for USB/CAN interface)
- NMotion CLI Tool (for configuration)
Electrical and Electronic Parts
- M8325s BLDC Motor with magnet (100KV, 8 pole pairs)
- 2Ω 50W Brake Resistor [For dumping regenerative current]
- Wires [26 AWG wire for DC+(Red) and DC-(Black)]
- CAN cables (2-pin JST PH, 2mm pitch)
- Type C USB Cable
Mechanical Parts
- Motor Mounting Plate
- Motor Mounting Setup (3D Printed)
- NDrive Z1 mounting Plate (3D Printed)
- 2040 Aluminium Frame
General Parts
- SHCS Allen Bolt M3x6mm x 6
- SHCS Allen Bolt M3x8mm x 4
- Button Allen Bolt M4x6mm x 4
- SHCS Allen Bolt M4x15 x4
- M4 Hex Nut x4
- M3 Spring T Nut x4
Tools and Supplies
- Allen Key 2.5mm and 3mm
- Screw Driver
- Wire Stripper
- Power supply (12–48V, 5A+ recommended)
Hardware Setup and Connections
With the components in place, the next step is to connect the M8325s motor, brake resistor, and power supply to the NDrive Z1. This section walks you through how to connect the M8325s 100 kV BLDC motor to the NDrive Z1, ensuring the setup is safe, secure, and ready for calibration.
- 1
Mount the NDrive Z1 to the NDrive Mounting Plate:
Mount the NDrive Z1 to the driver mount plate using 4 x SHCS M3x6 mm Allen bolts.
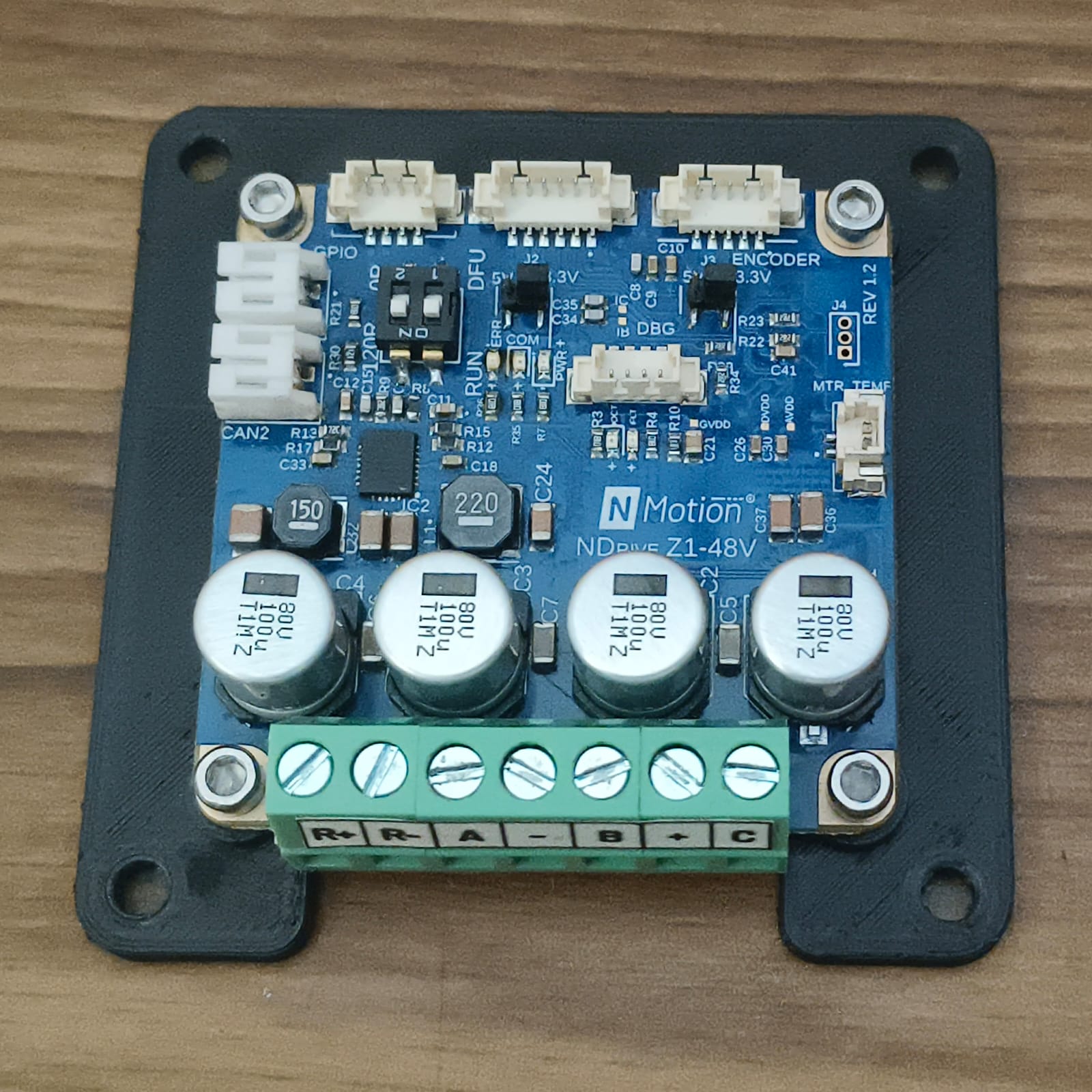
NDrive Z1 mounted to the mount plate - 2
Mount the NDrive Z1 Mount Plate to the Motor:
In this guide, we will be using the onboard encoder as the motor encoder, eliminating the need for external encoder wiring. We will be using the onboard encoder of NDrive Z1 with the magnet of M8325. Mount the driver to the back of the Motor using a 3D-printed mount plate, using M4x6mm Button Allen Bolts. Refer to the Mounting guidelines for more information. The NDrive Z1 features an onboard 14-bit absolute magnetic encoder (MA732).
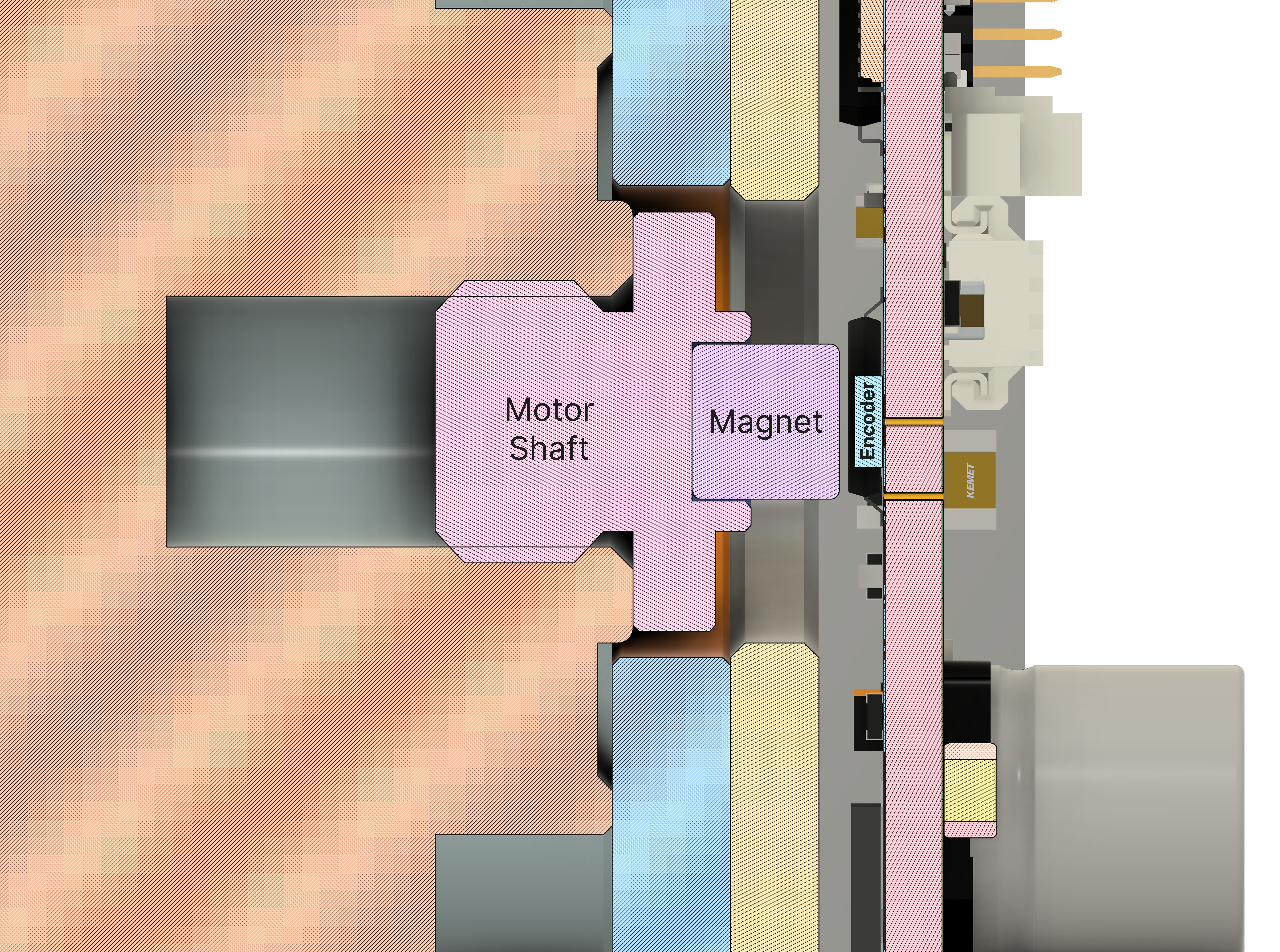
Distance between Magnet and NDrive's encoder IC surface should be at most 1 mm.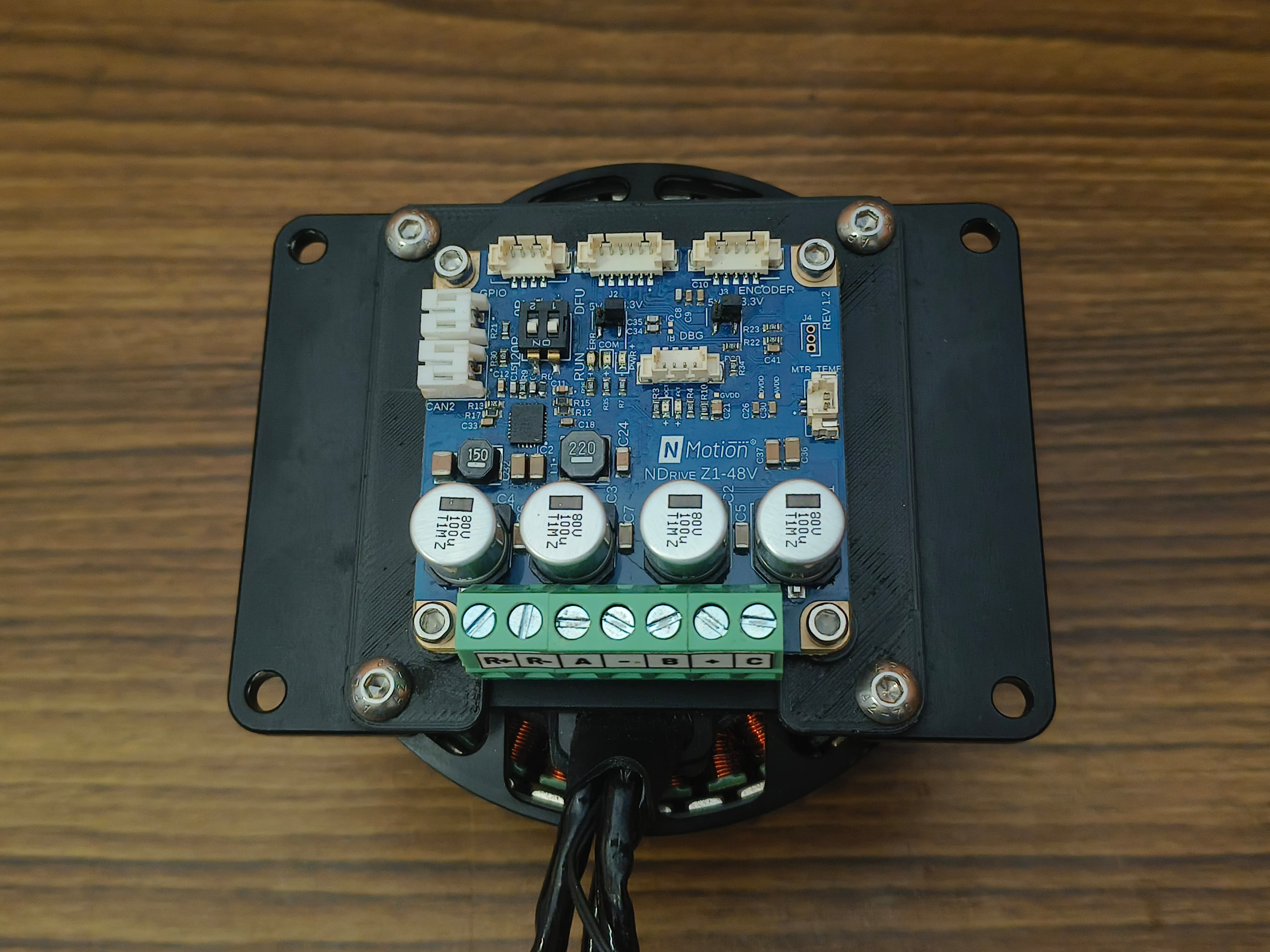 
NDrive Z1 mounted to the Motor - 3
Connect the Motor Wires, Brake Resistor and Power:
Wire the three motor phases from the M8325 to the NDrive Z1’s motor terminals A, B and C.
infoThe order of the phase wires is not important.
Connect the Positive of the Power Supply to DC+ and the Negative to DC- .
dangerEnsure that the power connection is made correctly, as a reverse polarity connection can damage the driver board.
Connect the 2Ω 50W brake resistor to the designated brake resistor terminals (R+ and R-) on the NDrive Z1. This safely dissipates regenerative energy, protecting your power supply during rapid deceleration of the motor.
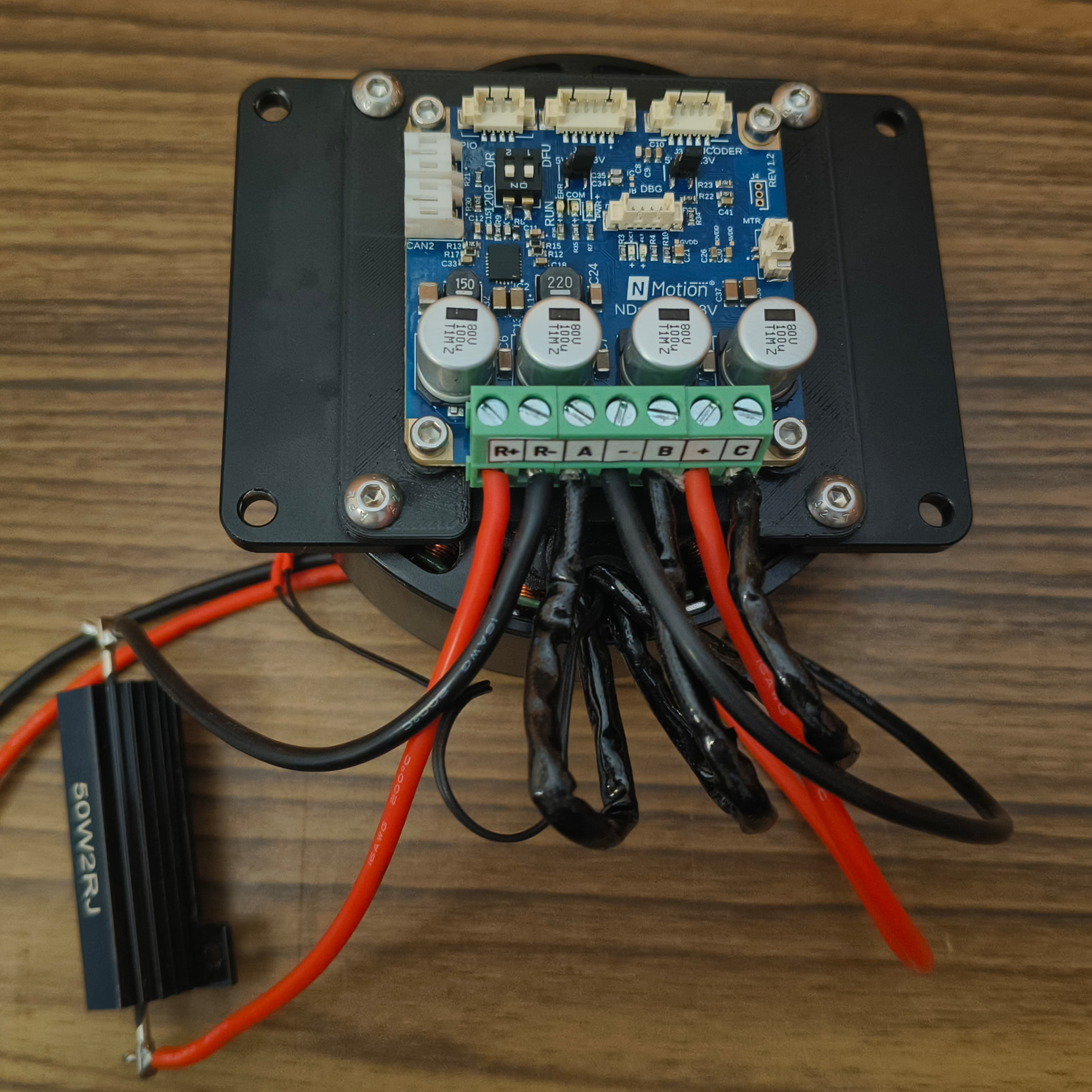

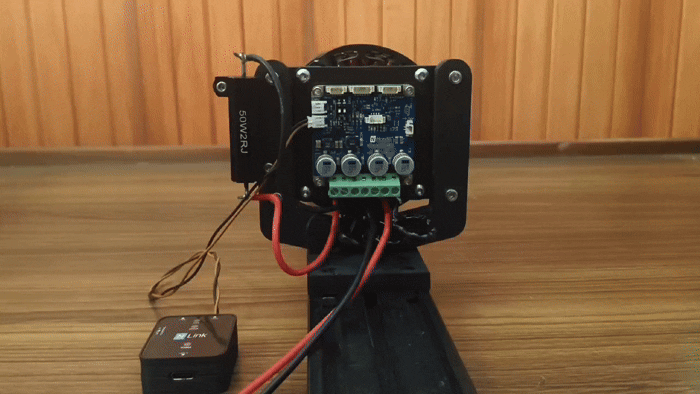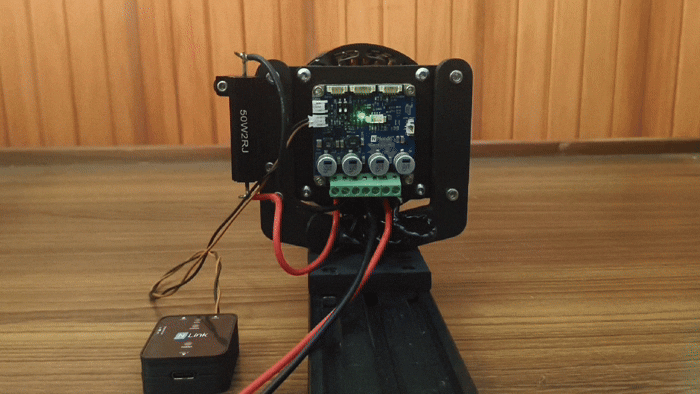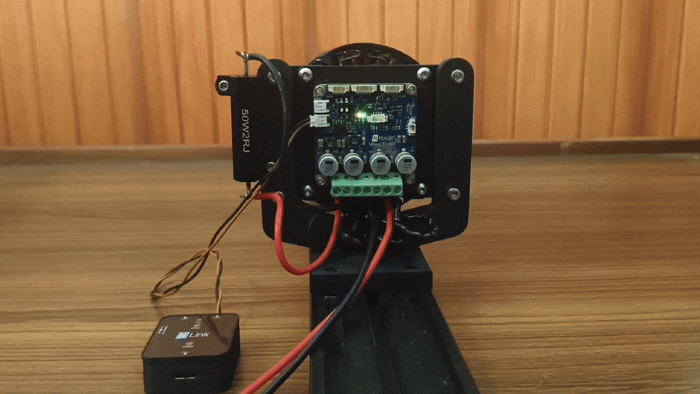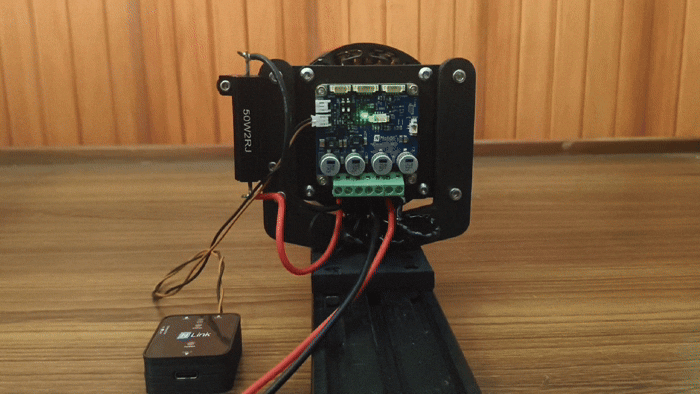
Motor Phases, Power, and Brake Resistor Connected to NDrive Z1 - 4
Communication:
Connect the NDrive Z1's CAN bus interface to the NLink Adapter using a 2-pin JST PH connector. The NDrive Z1 has a daisy-chainable CAN bus with two ports. Since only two devices are connected(NDrive and NLink), turn on the termination resistor switch in both NDrive and NLink. Refer to the CAN Bus connection and DIP Switch settings.
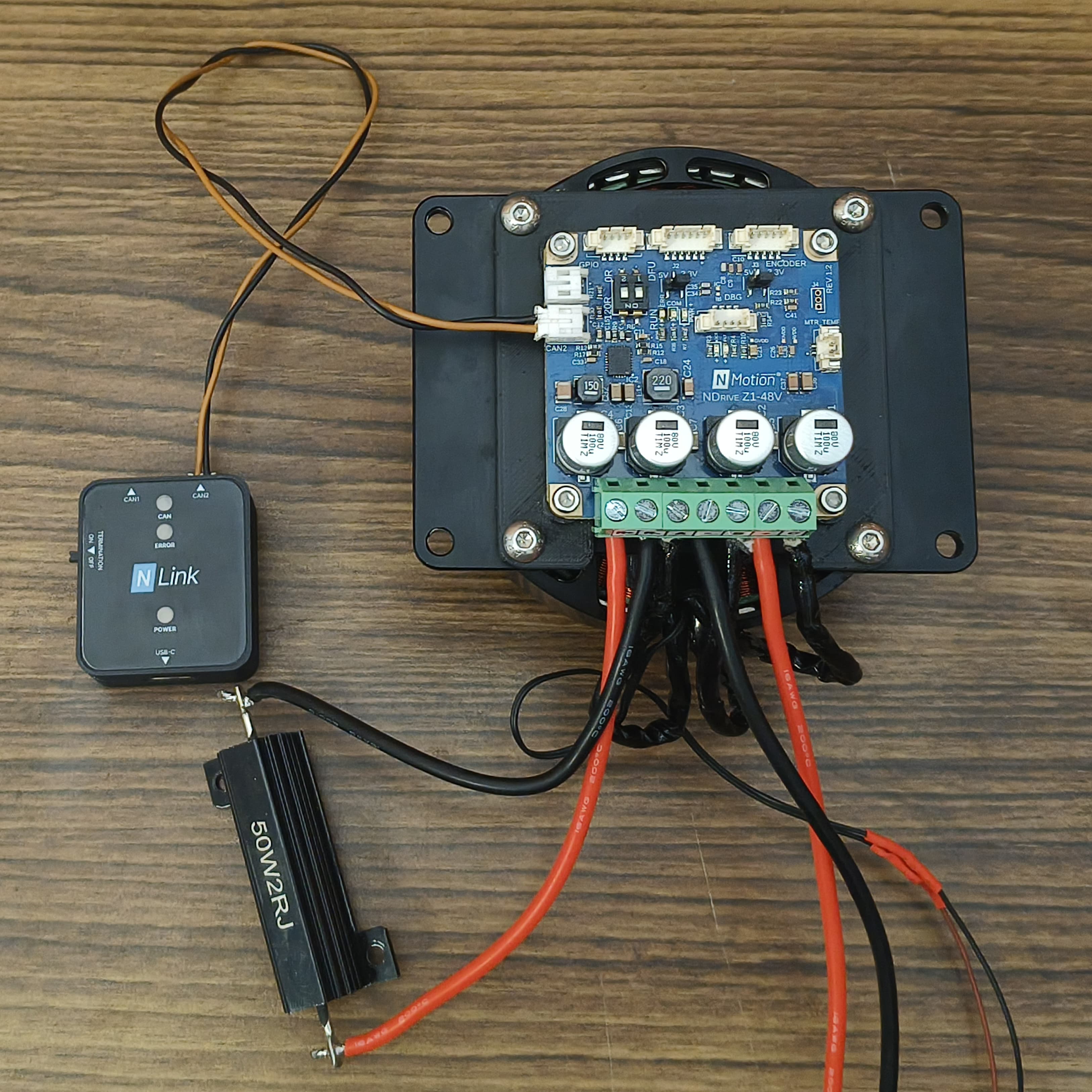
NLink Adapter Connected to NDrive Z1 - 5
Mount the motor-driver assembly onto the motor holding frame:
Mount the motor-driver assembly vertically onto the 3D-printed holding frame using four SHCS M4×15 mm Allen bolts and M4 hex nuts, ensuring the assembly is securely fastened and properly aligned. Mount the brake resistor onto the frame using two SHCS M3×6 mm Allen bolts. Once assembled, fix the base of the holding frame onto the 2040 aluminium extrusion using four SHCS M3×8 mm Allen bolts and M3 spring T-nuts, tightening the bolts evenly to maintain stability and alignment.
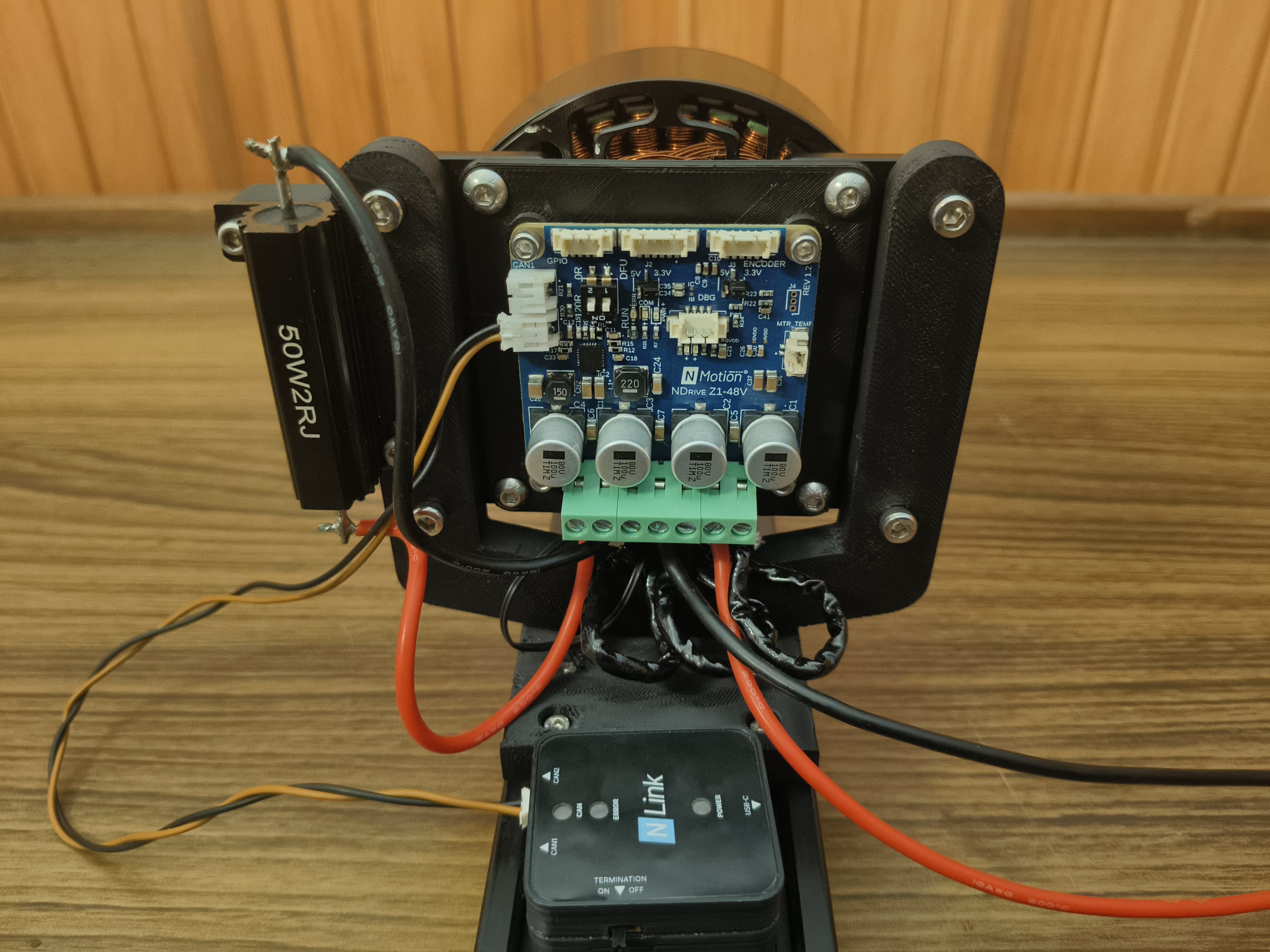
Wired Assembly of NDrive Z1 with M8325 BLDC Motor - 6
Connect to PC:
Plug the NLink Adapter's USB-C port into your system.

Final Assembly of NDrive Z1 with M8325 BLDC Motor
- Always make connections with the power supply turned off to avoid accidental shorts or damage.
- Never connect or disconnect the CAN cables while the NDrive Z1 is powered ON. Ensure the driver is completely powered OFF before making or removing any CAN connections to avoid potential damage to the communication hardware.
Configuring the NDrive Z1
The NMotion CLI is a powerful command-line interface for configuring and managing NMotion devices. It allows quick setup, calibration, and testing of the NDrive Z1 using simple commands, making configuration and performance monitoring efficient and user-friendly.
- 1
Install the NMotion CLI Tool:
Download and install the latest NMotion CLI tool on your computer.
- 2
Powering up the NDrive:
Turn ON the power to the driver. The COM LED (yellow) should blink during boot-up, indicating normal startup. If the LED does not blink, ensure that the DIP switch is configured to RUN mode.
Powering up NDrive Z1 - 3
Connect via NLink and Launch the NMotion CLI:
Plug the NLink adapter into your PC using a USB cable. Open a terminal and start the NMotion CLI.
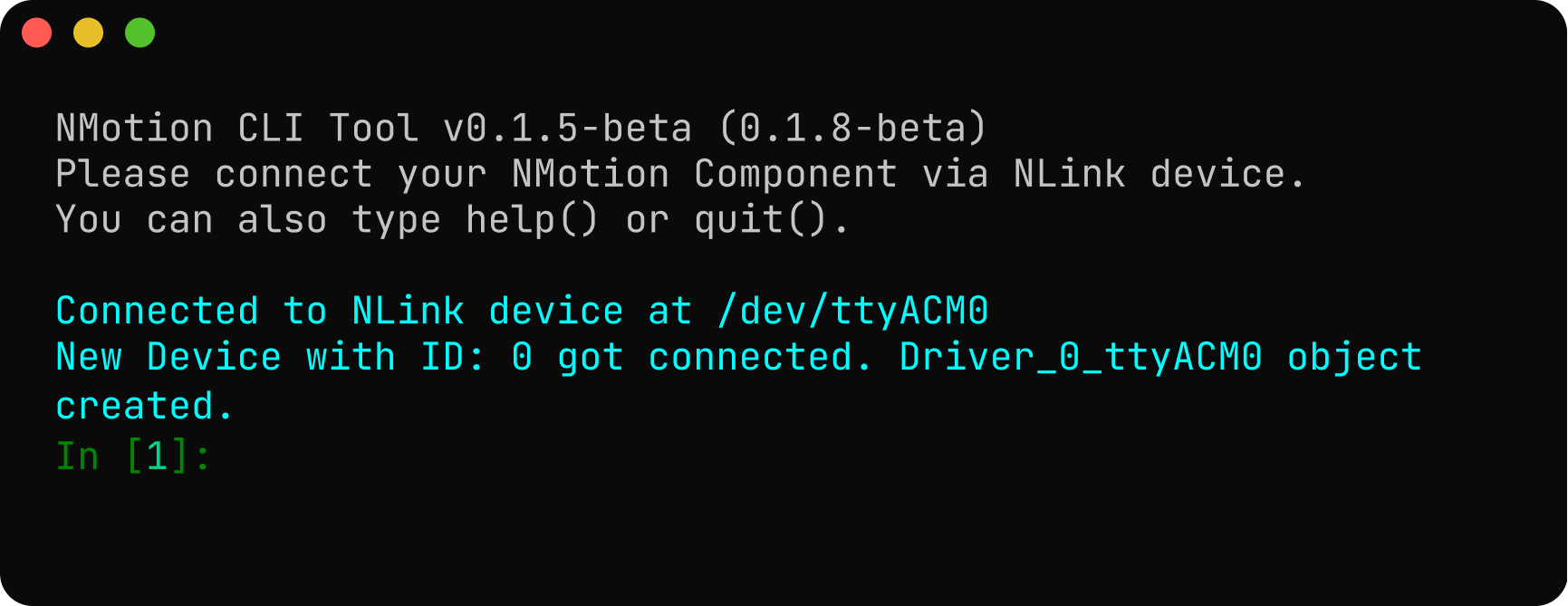
If everything is set up correctly, the NLink will be connected as a USB device, and its corresponding object will be created successfully. If the expected output is not displayed in the CLI Tool, refer to the troubleshooting guidelines to identify and resolve the issue.
When the driver is powered ON, the CLI automatically detects it and creates a corresponding object (e.g.,
Driver_0_ttyACM0) based on its default CAN Node ID. - 4
NMotion CLI API Functions
The configuration can be written using set commands and can be read using get commands. Refer API Documentation for more details.
- 5
Configure CAN Bus:
It is crucial to assign a unique CAN Node ID to the driver, especially if multiple devices are on the CAN bus. The default ID is 0. You can change it using the
setNodeId()function.Note: Setting the CAN Node ID will cause the driver to disconnect and reconnect as a new object name in the CLI (e.g., from
Driver_0_ttyACM0toDriver_10_ttyACM0if you set the ID to 10). To save the new node, save the node ID using thesave_configuration()function. After the command, the driver will save and reboot.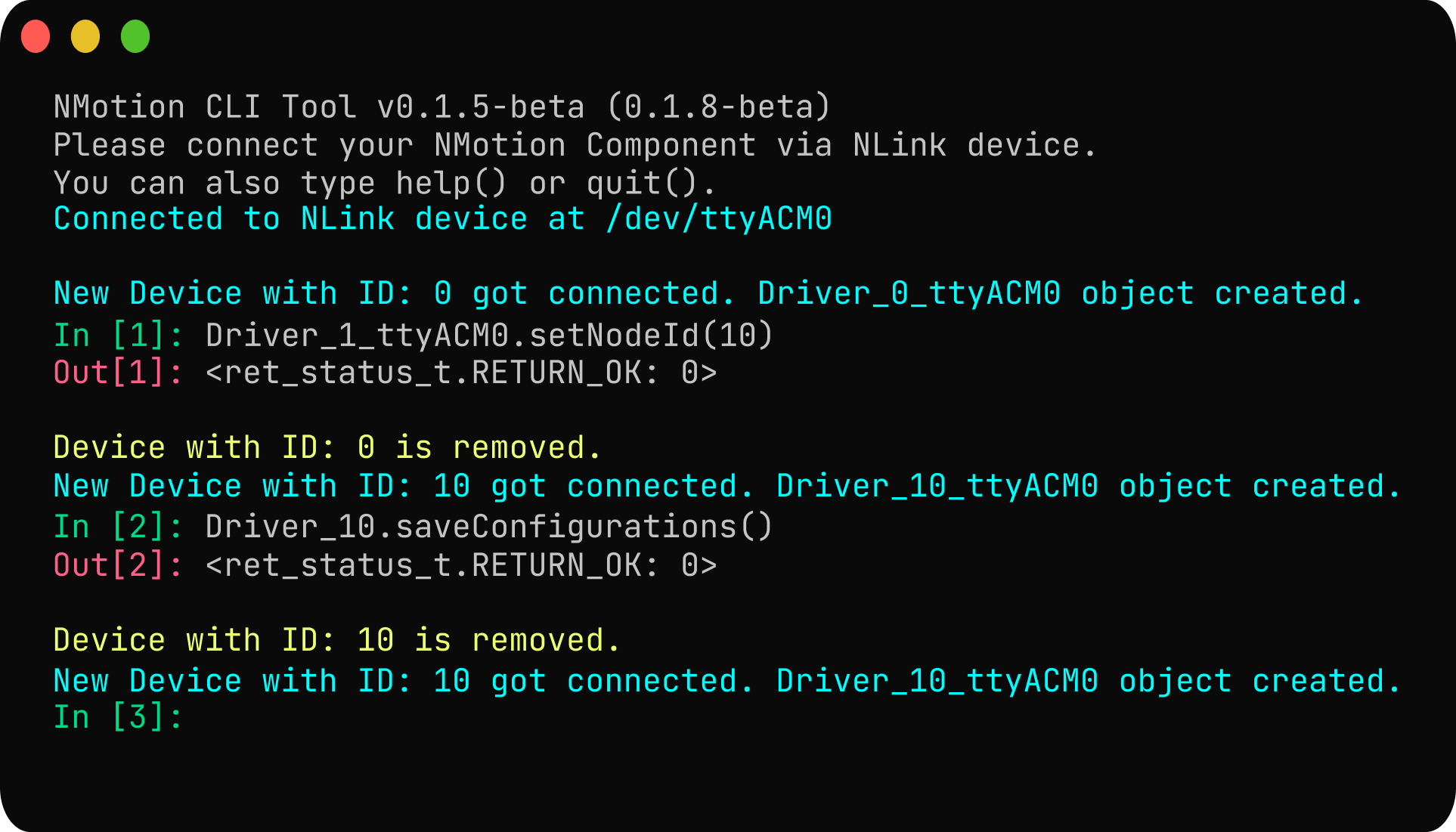
- 6
Power Configuration:
Configure the under-voltage and over-voltage trigger levels. The driver will trigger a voltage trip error if the voltage goes below the under-voltage trip level and above the over-voltage trip level. The under-voltage trigger level is configured as 10V, and the over-voltage trigger level as 56V. A 2-ohm brake resistor is connected to the driver, and its value can be configured and enabled using
Driver_10_ttyACM0.enableBrakeResistor(brake_resistance_value). Configure the regenerative current to 0 usingDriver_10_ttyACM0.setRegenCurrentTripLevel(0).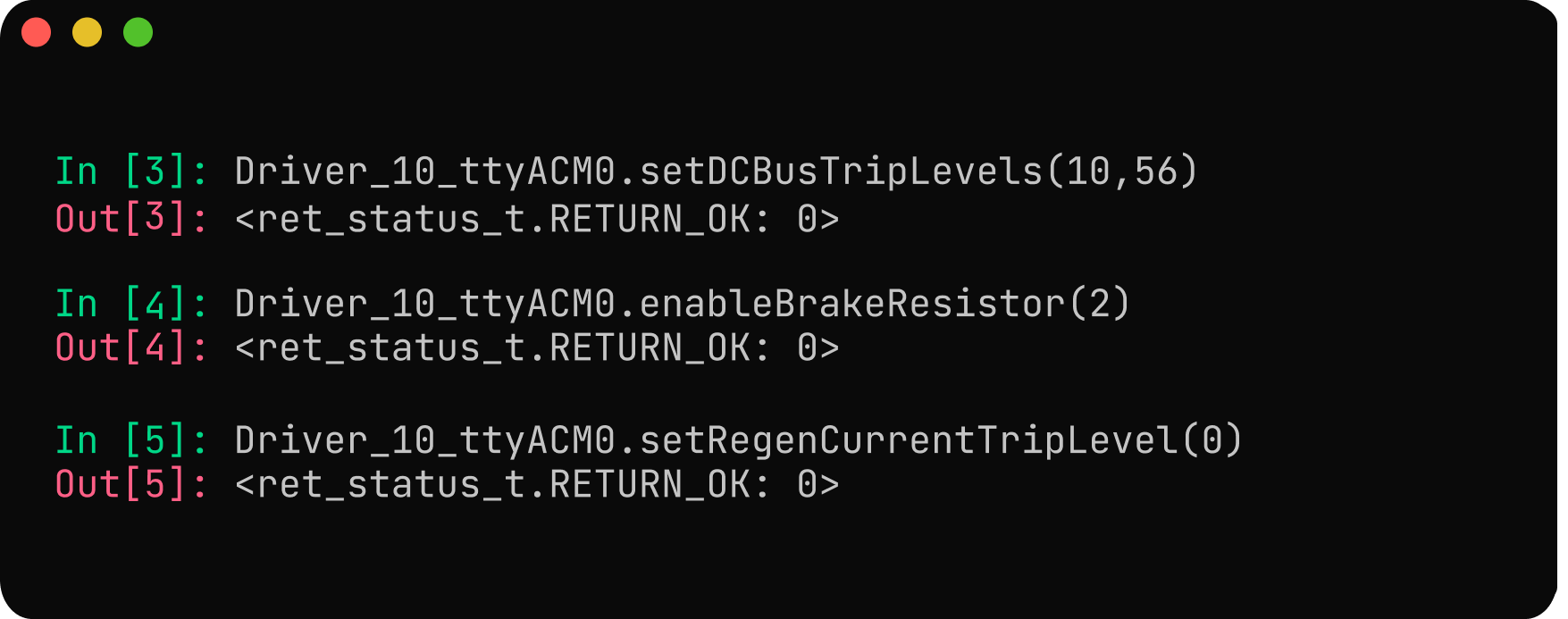
- 7
Motor Configuration:
Use Driver to configure the motor parameters such as pole pairs, kV rating, and current limit using
Driver_10_ttyACM0.setMotorParameters(pole_pairs, kV_rating, current_limit). For the M8325 100 kV BLDC motor, the pole pair is set to 20, and the kV rating is set to 100. Set the current limit to 55A.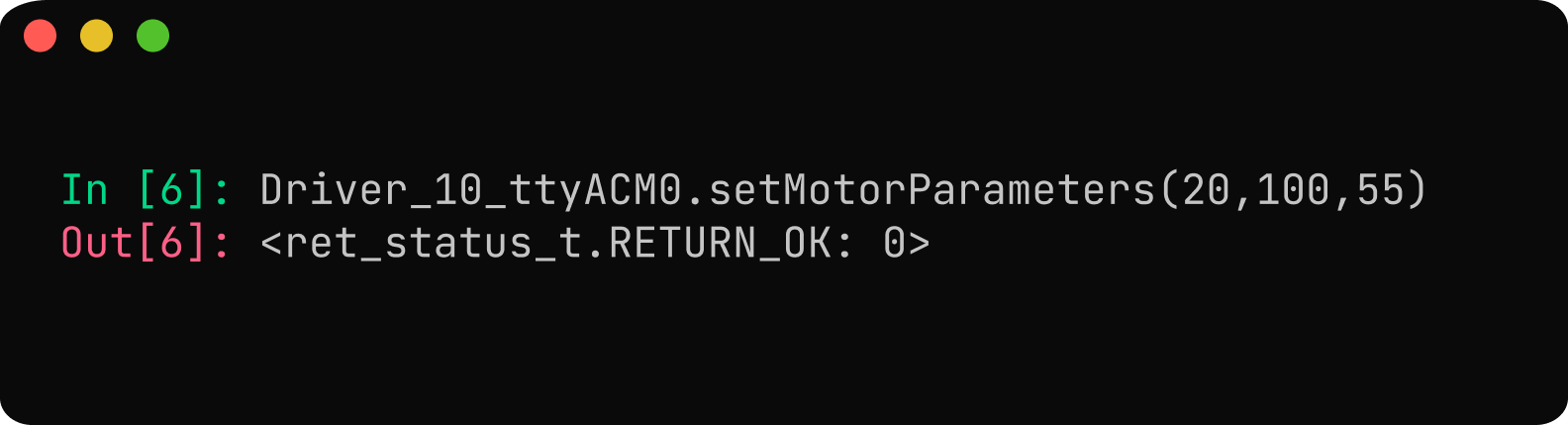
- 8
Encoder Configuration:
Use
Driver_10_ttyACM0.configureMotorEncoder(1, 16384)to configure the onboard absolute encoder as the motor encoder. The encoder_type for the onboard absolute encoder would be 1 (TYPE_ONBOARD_ENCODER). The onboard encoder's resolution is 14 bits. Remember to save the configuration for the encoder settings to take effect.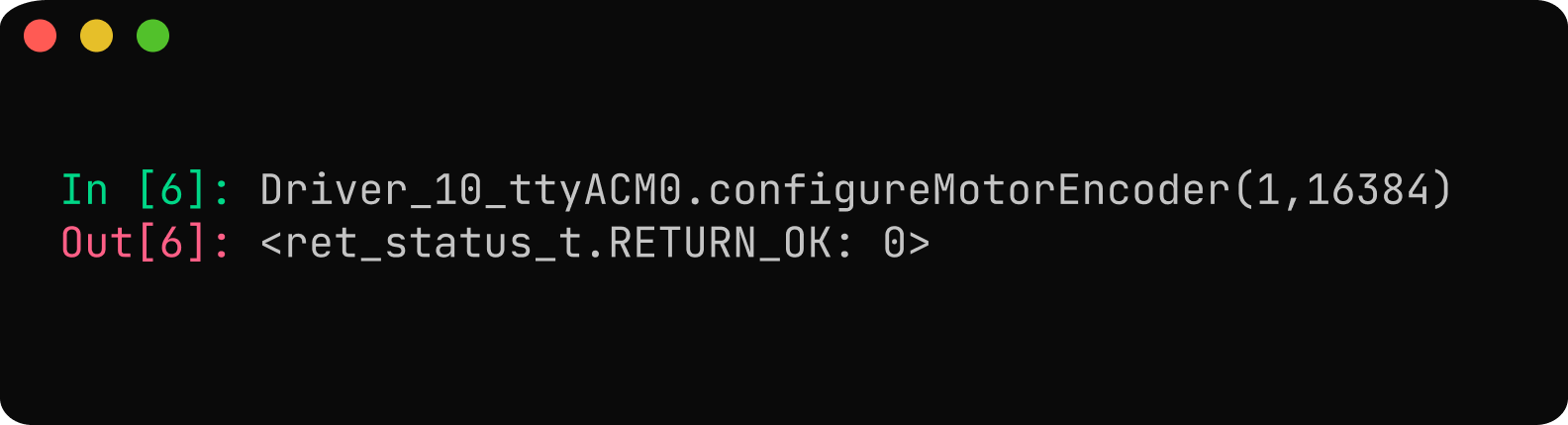
- 9
Calibration Configuration:
The default calibration parameters are 2V for calibration voltage and 10A for calibration current, which can measure up to a phase resistance of 0.2 ohms. The default configurations are suitable for the M8325 BLDC motor. Refer setting calibration parameter.
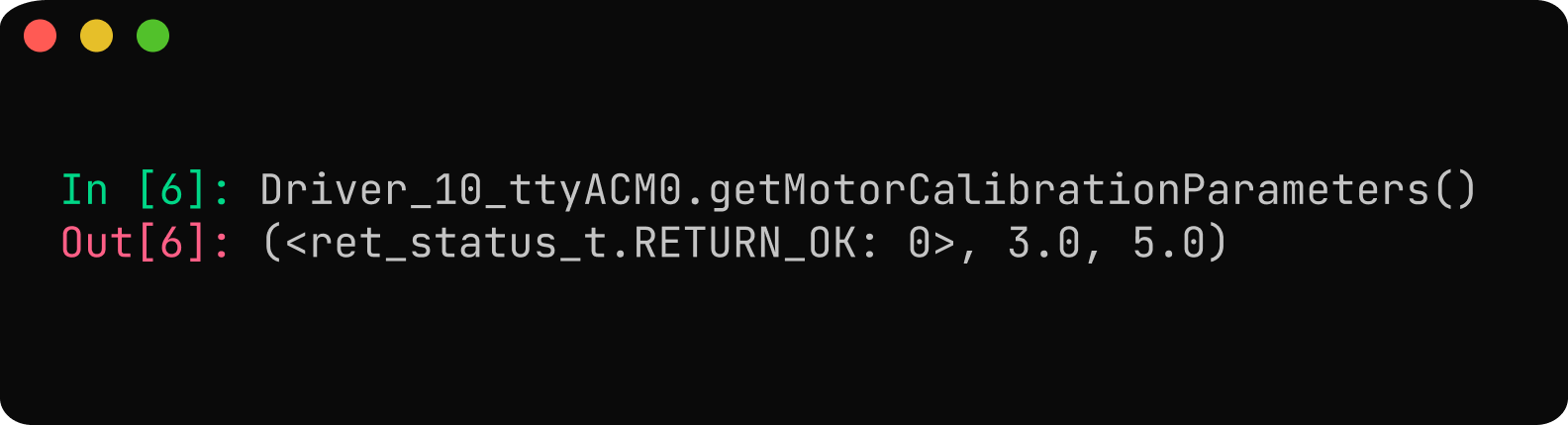
- 10
Save Configuration:
After setting all parameters, save them to the driver's non-volatile memory using
Driver_10_ttyACM0.saveConfigurations(). This ensures settings persist after reboot. Saving triggers a reboot. Be mindful that the non-volatile memory has a limited number of write cycles, so avoid saving too frequently.
Calibrating NDrive Z1 with Motor
Before running the calibration sequence, ensure that the motor is free to move and all loads are disconnected. Also, ensure that the motor and power connections are properly connected and the driver is properly mounted.
Initiate the calibration sequence by using Driver_10_ttyACM0.runCalibrationSequence() command.
During the calibration, the NDrive Z1 measures motor phase parameters, determines the encoder offset, and verifies the configured pole-pairs and counts per revolution (CPR). The motor will draw some current and emit a short beep during the inductance measurement phase, followed by slight rotations in both directions for encoder offset calibration.
If no errors occur, the NDrive Z1 has been successfully calibrated with the motor. Save the calibrated configuration to complete the process—your NDrive Z1 is now ready for motor control.
If any error is triggered, the error LED (RED) will be ON. You can check the specific error code using Driver_10_ttyACM0.getErrorCode() function and then refer the Error Handling section for troubleshooting the issue.
Operation
After calibration, the motor can operate in various control modes such as position, speed, and torque. Here, the motor is commanded to move to an angle of 180 degrees at a speed of 60 degrees per second.
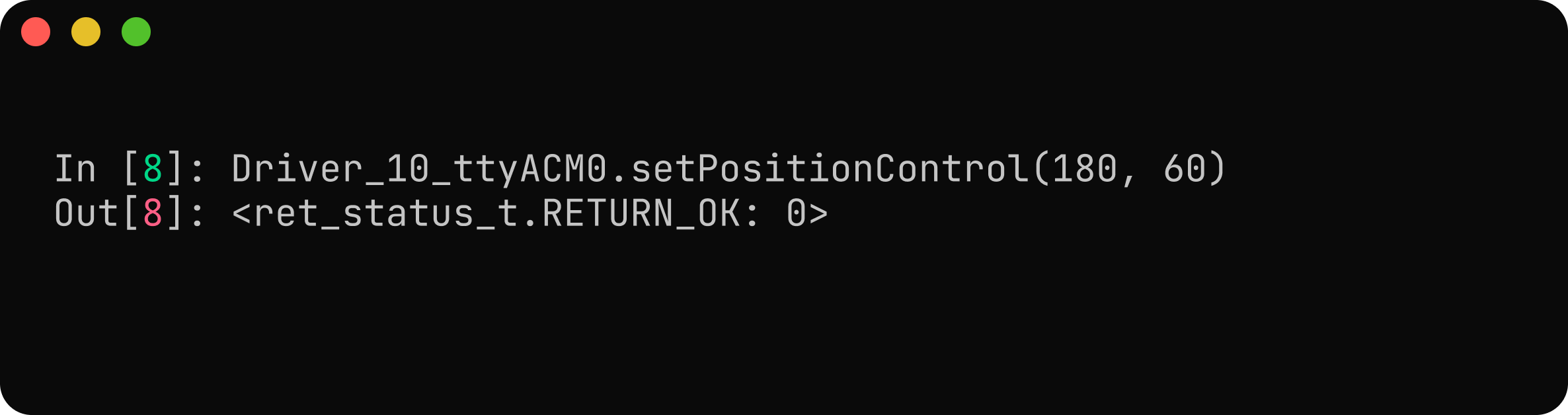
By completing the hardware setup, configuration, and calibration steps, the M8325 BLDC motor is now integrated with the NDrive Z1 and ready for use. The system is configured to use the onboard absolute encoder, power handling is set up correctly, and the driver is calibrated through the NMotion CLI.
For deeper insights, expanded capabilities, or further assistance, feel free to explore our documentation or get in touch with our support team.